Motorcycle Battery Voltage Drops When Starting – Know the Reasons
Instead of a satisfied engine roar, meeting with a sluggish start-up and a noticeable drop in battery voltage is a common phenomenon for bikers.
But why does motorcycle battery voltage drop when starting? The following are the main reasons for the issue:
- Lack of charge
- Aging battery
- Corrosion in the terminals
- High internal resistance
- Extreme temperature conditions, etc.
When looking closely at the matter, other crucial aspects come to pass. In this article, I’m going to discuss the leading cause, DIY fixing attempts, and prevention measures in detail.
Why Does Motorcycle Battery Voltage Drop When Starting?
Out of numerous grounds, some anticipation of the key reasons why the voltage drop happens is a few.
Here are the most common causes:

Battery Requires Charging
The lack of charging is a major and overlooked reason for the voltage drop in a motorcycle battery. Natural self-discharge occurs when a motorbike is left alone for a long time. It’s a common phenomenon for anything that retains electrical charge.
In addition, if you don’t charge up your motorcycle battery routinely, lead sulfate crystal builds up on the battery plates. That reduces electric potential. Hence cripples the battery’s ability to retain charge.
Aging Battery
Like other electrical components, the battery loses efficiency as it gets older. That means even though your motorbike’s battery provides voltage, it cannot retain that voltage under load. Not enough to exact.
It happens due to sulfation and damage to individual cells inside the battery, creating an imbalance. This can also happen due to corrosion, internal resistance, and overall wearing. I’ll get back to them in detail later on.
Anyway, when high electrical demand takes place, such as the start of the vehicle, the battery’s lackluster efficiency is uncovered. Hence, you see a voltage drop.
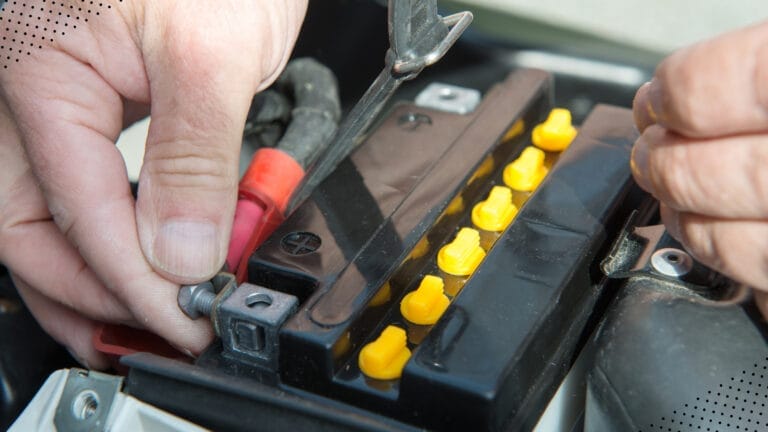
Corroded Battery Terminals
If the battery terminals get affected by corrosion, expect a voltage drop while starting your motorbike.
The chemical reaction between the metal terminals over time and the surrounding environment is all responsible for this.
Electrodes in the battery are submerged in an electrolyte made of sulfuric acid and water. If there’s any leak, it will facilitate an acidic environment. As a result, corrosion happens with the metal, and it slowly breaks down.
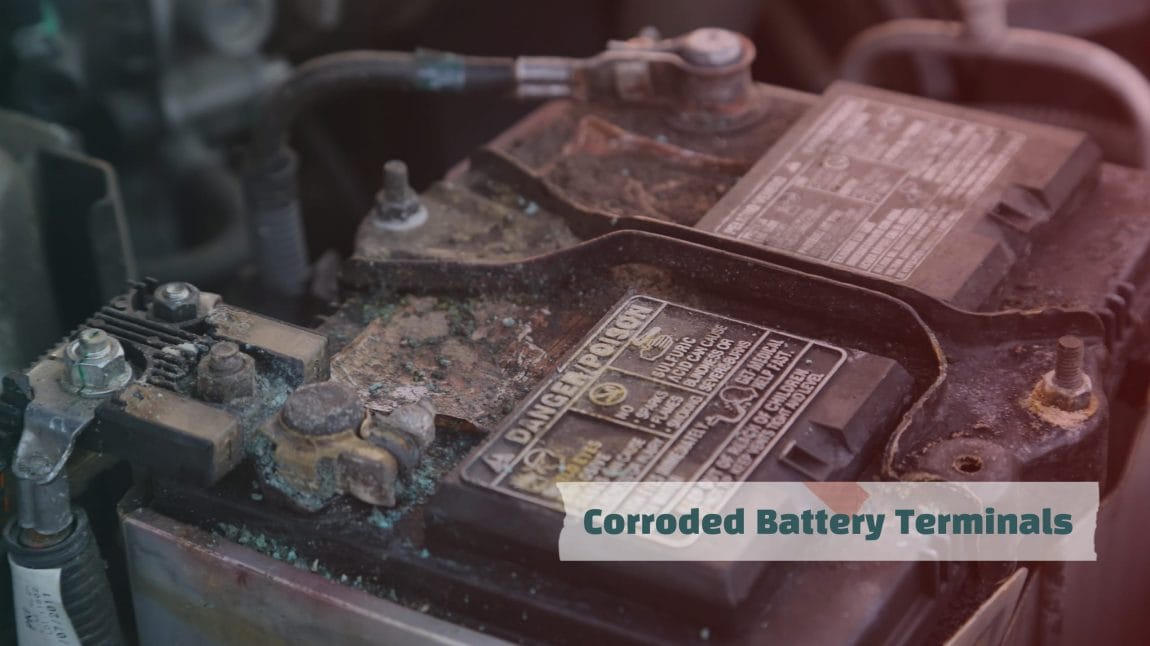
Not to mention, charging a lead-acid battery can produce hydrogen gas. This gas can escape if the vents are not in good condition. And react with the metal terminals, leading to corrosion.
Also, environmental moisture gathers around the battery terminals during the rainy season, especially if the motorcycle is idle for a long time. Along with it, airborne contaminants participate in accelerating corrosion.
Trickle Charged Battery
Trickle charge means low but constant current supplied to the battery for an extended period. It is done to retain the charge when the motorcycle is not in use.
Now, during the trickle charging process, the battery accumulates an electromotive force (EMF). This represents the battery’s ability to provide necessary electrical energy.
When you start the bike, the battery’s internal resistance becomes a limiting factor. As a result, this resistance and a sudden current draw lead to an abrupt voltage drop at the start.
Internal Resistance
The starter motor requires a high current at the initiation of the motorcycle to generate sufficient torque. Otherwise, the engine’s crankshaft won’t rotate.
In the process of creating the rotational force, high current draw and resistance conflict with each other, and so does the voltage plummet.
Effect of Temperature
Believe it or not, the temperature has a cardinal effect on motorcycle battery voltage. Lower ambient temperature affects the chemical and physical processes within a motorcycle battery.
This includes increased internal resistance, lessened electrochemical activity, and reduced overall capacity.
Moreover, in cold temperatures, viscosity increases in the engine oil. So, more power is required to turn the engine, which puts an additional load on the battery.
How Do You Know Motorcycle Battery Voltage Has Dropped?
Identifying voltage drops is crucial to take proper measures and ensure the battery’s longevity. To understand this, you should look out for the following signs on your motorcycle:
- Check whether the dashboard headlights appear dimmer while starting the motorcycle. It’s a major sign of voltage drop.
- Observe any sign of a slow or weak start during the ignition. It means the engine crank will be slower and have a poor spark.
- If the engine does not start and you hear a rapid clicking sound, that is due to insufficient voltage from the battery.
- Failure of the horn, indicators, or other electronic components might indicate a voltage decline.
- Connect a multimeter to the battery terminals and measure the voltage. It should be around 12.6 volts for a fully charged battery. If you get a reading significantly below that, it’s a problem.
How Do You Fix Voltage Drops in Motorbike Batteries?
Some DIY steps can fix the voltage drop with your bike’s battery. It can save quite a few bucks, to say the least.
Here’s how you can attempt to solve voltage drop in motorcycle battery:
- Remove the battery from the motorcycle. Check the terminals. If you see any corrosion and other particles, clean them up. Use a wire brush, baking soda, and water for an effective rinse.
- After cleaning the terminals, inspect the screws on them. Tighten them along with the starter motor, solenoid, and ground connection screws.
- Visually observe the wirings of the battery. Look out for damage or fraying. Replace the cables to solve this issue.
- Inspect your motorcycle battery’s charging system. Use a multimeter to check whether the voltage is around 13.5 to 14.5 volts while the engine runs. Mind you, the issue lies within the alternator, regulator, or wiring if you don’t see voltage around the stated number.
If it is impossible to diagnose or fix from your end, seek professional help. When every other trick fails, it might be time for you to replace the battery. Depending on the bike, it may cost $75 to $300.
See the following video on how to test a motorcycle battery with a multimeter.
What Is the Correct Battery Voltage to Start the Bike?
At the time of initiating a bike, the battery voltage needs to meet a particular threshold. This varies depending on the motorbike type and model.
You see, a perfectly fine motorcycle battery should rest above 12.20V. And during start-up, falling down between 11V and 10.5V is completely normal. After that, once the engine keeps rolling, you should expect battery voltage anywhere between 12 and 14.5.
Bear in mind that anything above 14.8V screams potential issues with the battery. It’s basically overcharging due to the underlying problems.
Prevent Voltage Fluctuation in Motorcycle Battery
You can stop all the complications with the battery if you are careful enough. It just requires some preventive measures. It will reduce labor and money, to say the least.
- Keep the battery away from extreme temperatures such as too hot or cold.
- Do not overload the electrical system by attaching extraneous accessories. Turn them off when not in use.
- Maintain a proper battery charge state by charging it regularly and avoid deep discharges or overcharging.
- Regularly check the battery terminals for corrosion and loosened connections and clean them up.
Frequently Asked Questions
When peeking into the matter of motorcycle batteries, quite a few common questions popped up on my radar. As an owner, you should know the answers.
Is A Battery Healthy If It Drops Under 10 Volts With Load?
No, if your motorbike battery voltage drops under 10V, it signifies poor health. A good-condition battery should not go under 10V in any circumstance. When you see such a drop, pay special attention as it might be a serious issue and will hinder performance.
Can Voltage Drop Cause Weak Cranking on Motorcycles?
Yes, lower voltage can cause below-par cranking on motorcycles. Insufficient difference in potential between the two battery terminals impedes the motor’s ability to rotate it. That results in a slow crank.
Closing Thoughts
The surge in electrical current required for ignition puts a heavy load on the battery for a brief period of time. When the battery condition is not good, a voltage dip occurs.
With that said, this situation is manageable with regular maintenance and timely replacements. Once you understand the natural process of a motorcycle, you can hit the road without missing a bit!







