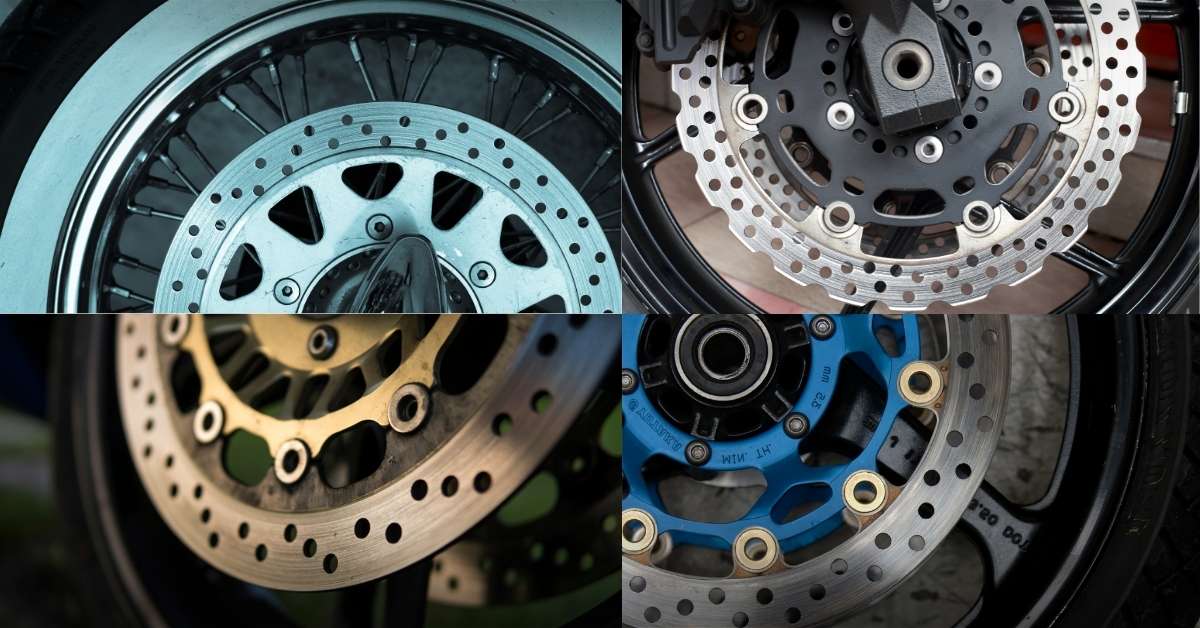
How Long Do Motorcycle Brake Discs Last?
Ever wondered if your motorcycle’s brake discs are still in their prime or if it’s time to replace them? Knowing how long brake discs last can be the difference between smooth rides and dangerous stops.
Properly maintained, brake discs can last between 20,000 to 50,000 kilometers, depending on factors like riding style and road conditions. Aggressive braking, wet or gritty roads, and lack of regular cleaning can shorten their lifespan. Always check for signs of wear, such as grooves, warping, or reduced braking efficiency, to keep your rides safe.
In this guide, we’ll uncover the factors that affect brake disc lifespan, signs of wear, and how to maximize their durability.
Ready to keep your motorcycle performing at its best? Download our free brake maintenance checklist at the end of this article and ensure your safety on every ride
Table of Contents
Understanding Motorcycle Brake Discs
Motorcycle brake discs are essential for safe and efficient braking. These circular metal components, usually made from stainless steel or cast iron, work with brake pads to create the friction needed to slow down or stop your bike.
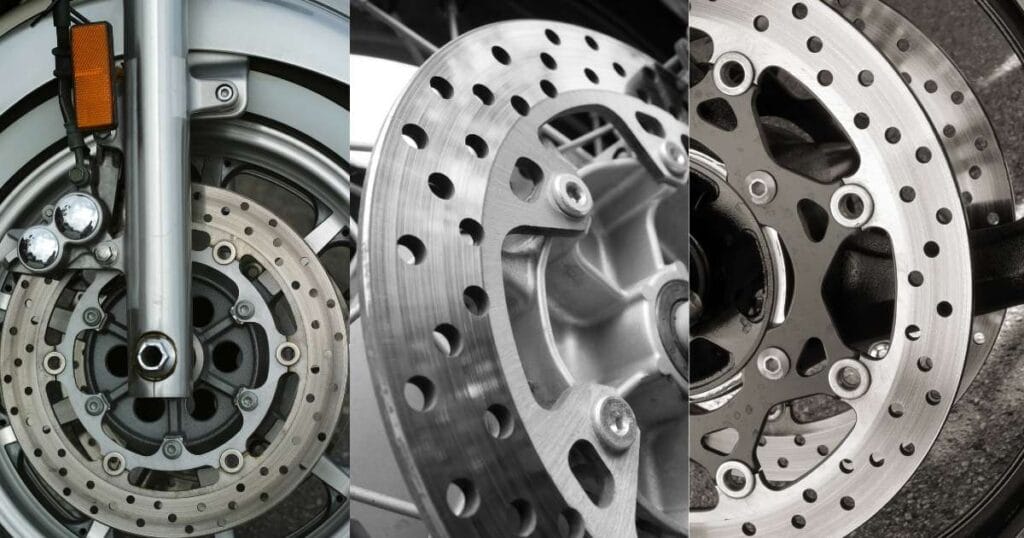

When you squeeze the brake lever, the pads press against the rotating disc, converting your bike’s momentum into heat, which dissipates to bring the motorcycle to a stop.
There are different types of brake discs, each designed for specific riding styles:
- Solid Discs: Common on commuter bikes, offering consistent performance but prone to heat buildup.
- Ventilated Discs: Feature drilled holes or slots for better heat dissipation, ideal for high-speed or touring bikes.
- Wave Discs: Lightweight with wavy edges to reduce weight and improve cooling, popular for sport bikes.
The material of the disc plays a significant role in performance. Stainless steel is durable and rust-resistant, while high-end options like carbon-ceramic are lighter and handle extreme heat better but come at a higher cost.
How long do motorcycle brake discs last
Motorcycle brake discs can typically last between 20,000 to 50,000 kilometers (approximately 12,000 to 30,000 miles), or around 2 to 5 years of regular use. However, the exact lifespan varies significantly depending on how the motorcycle is used.
Casual Riders:
For riders who use their motorcycles primarily for weekend cruises or occasional rides, brake discs can often last closer to the 50,000 km mark, or about 4 to 5 years. The lighter use and gradual braking patterns associated with leisure riding put less stress on the discs, allowing them to wear more slowly.
Sports/Racing Bikes:
On the other hand, sport and racing bikes experience much more intense braking, often at high speeds and under greater stress. In these cases, brake discs may only last around 20,000 to 30,000 kilometers, or about 1.5 to 3 years. Frequently, heavy braking and high temperatures generated on tracks or aggressive rides can cause faster wear and potential warping.
Commuters:
For daily commuters, who deal with stop-and-go traffic and varied road conditions, the lifespan of brake discs typically falls in the middle range, around 30,000 to 40,000 kilometers or roughly 2 to 4 years. While the constant braking in urban areas does lead to wear, it’s generally less intense than racing conditions.
These estimates are based on general observations from motorcycle maintenance experts and rider feedback. Regular inspections and proper care can help extend the life of your brake discs, regardless of your riding style.
Factors That Affect the Lifespan of Motorcycle Brake Discs
Understanding what influences the wear and tear of your motorcycle’s brake discs can help you prolong their lifespan and ensure your safety on the road. Let’s dive into the key factors that can either extend or shorten their durability.
Material Quality
The material used in brake discs has a significant impact on their longevity:
- Stainless Steel: Most commonly used due to its resistance to rust and decent heat management. It provides a balance between durability and cost-effectiveness.
- Cast Iron: Known for its excellent heat dissipation, which reduces the risk of brake fades during intense use. However, it’s heavier and prone to rust, making it less suitable for wet environments.
- Carbon ceramic discs: These discs are found on high-performance motorcycles and are incredibly heat-resistant and lightweight. However, they come with a premium price tag. They’re best for riders who need top-tier performance, like track enthusiasts.
Riding Style
How you ride plays a crucial role in determining how long your brake discs will last:
- Aggressive Braking: Riders who frequently brake hard—especially in sport riding or racing—put more stress on their discs, causing them to wear down faster. The heat generated during sudden stops can warp the discs over time.
- City Commuting: Constant stop-and-go traffic means more frequent braking, which gradually wears out the discs. However, this wear is usually more evenly distributed than that from aggressive, high-speed riding.
- Long-Distance Touring: While highway cruising typically involves less braking, the increased weight from luggage can add pressure on the discs, especially during downhill braking.
Road Conditions
The surfaces you ride on can be unforgiving on your brake discs:
- Wet and Muddy Roads: Water can cause temporary surface rust on discs, while mud and debris can act like sandpaper, speeding up wear. Always clean your discs after riding through muddy conditions.
- Sandy or Gritty Roads: Sand particles can get lodged between the brake pads and discs, causing scratches and accelerated wear. These tiny abrasions might not be visible right away but can reduce braking efficiency over time.
- Uneven Terrain: Off-road riders often experience increased disc wear due to constant exposure to dirt and grit and frequent braking on slopes.
Maintenance Habits
Routine care can significantly extend the life of your brake discs:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust, dirt, and brake pad residue can accumulate on the disc surface, reducing braking efficiency and increasing wear. Cleaning the discs periodically with the right products ensures smooth operation.
- Inspection: Checking for signs of wear, such as grooves, warping, or discoloration, can help you catch issues early. If left unchecked, worn discs can compromise your braking power, especially in emergencies.
- Proper Storage: If your bike sits unused for long periods, moisture can build up on the discs, leading to rust. Using a cover and storing your bike in a dry place helps prevent this.
Weight of Motorcycle and Rider
The combined weight of the rider, any passenger, and added gear can put additional pressure on the braking system:
- Heavier Loads: A fully loaded touring bike or riding two-up adds more force to the braking process, causing the discs to heat up faster. This extra heat can lead to quicker wear and even warping under heavy braking.
- Lightweight Bikes: On the other hand, lighter bikes with single-disc setups generally experience less stress, which can result in longer disc life.
Type of Brake Pads Used
The type of brake pads you choose directly affects how your brake discs wear:
- Organic Pads: These are softer and create less friction, resulting in smoother braking but shorter pad life. They’re gentle on discs, which can extend disc longevity.
- Sintered Pads: Made of metal particles fused together, these pads offer superior braking performance, especially in wet conditions. However, their abrasive nature can wear down discs faster.
- Ceramic Pads: Known for their longevity and heat resistance, ceramic pads are easier on discs than sintered pads but still provide solid stopping power. They’re ideal for riders who want a balance between performance and disc preservation.
Environmental Conditions
Temperature and humidity also affect how brake discs perform over time:
- Heat: Excessive heat from frequent braking can cause brake discs to warp or develop hot spots. This is especially true in hotter climates or during long downhill descents.
- Humidity: High humidity can lead to surface rust if the discs are exposed to moisture for extended periods. While stainless steel discs are less prone to rust, they’re not entirely immune.
- Cold Weather: In colder temperatures, discs may take longer to heat up, potentially affecting their efficiency. However, cold weather alone doesn’t cause wear; rather, it’s the thermal shock from rapid heating and cooling that can lead to cracks.
By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions to extend the lifespan of your brake discs. A combination of good riding habits, regular maintenance, and choosing the right components can help you get the most out of your motorcycle’s braking system, ensuring safety and performance on every ride.
Signs That Your Brake Discs Need Replacement
Knowing when to replace your motorcycle brake discs is crucial for maintaining safe braking performance. Unlike other components that might simply wear out, faulty brake discs can compromise your stopping power, putting you at serious risk. Here are clear signs that your brake discs are due for replacement:
- Deep Grooves or Scoring: Visible grooves or ridges on the disc surface indicate excessive wear and reduced efficiency.
- Below Minimum Thickness: If the disc measures below the manufacturer-specified thickness (3-3.5mm), it’s time for a replacement.
- Warped Disc: Vibrations or pulsations during braking suggest the disc is warped and no longer providing even pressure.
- Cracks or Visible Damage: Any cracks, chips, or deformities on the disc compromise its structural integrity and require immediate replacement.
- Uneven Pad Wear: If brake pads are worn unevenly, it may indicate disc warping or improper contact, signaling the need for a new disc.
How to Prolong the Life of Your Motorcycle Brake Discs
Extending the lifespan of your motorcycle’s brake discs is not just about saving money—it’s about ensuring your bike’s braking system remains reliable and safe. By incorporating some simple practices into your regular maintenance routine, you can get the most out of your brake discs. Here’s how:
- Avoid Hard Braking: Use smooth, gradual braking instead of frequent hard stops to minimize disc wear and overheating.
- Check Brake Pads Regularly: Replace worn pads promptly to prevent them from damaging the disc surface.
- Clean the Discs: Regularly clean discs with a brake cleaner to remove dirt, debris, and oil that can accelerate wear.
- Use the Right Brake Pads: Ensure the brake pads are compatible with your discs to avoid uneven wear or damage.
- Inspect for Damage: Regularly check for cracks, grooves, or warping and address issues early to prevent further deterioration.
- Avoid Overloading: Reduce excessive weight on your bike to lessen the strain on the braking system and discs.
- Maintain Proper Riding Habits: Use engine braking when possible to reduce reliance on the brake system.
Comparison of OEM vs. Aftermarket Brake Discs
When it comes time to replace your motorcycle brake discs, you’re faced with a choice: stick with Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts or opt for aftermarket discs. Both have their advantages and drawbacks, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your riding style, budget, and performance expectations. Let’s break down the differences to help you decide which option is best for your needs.

What Are OEM Brake Discs?
OEM brake discs are parts made by the original manufacturer of your motorcycle or by a company that the manufacturer has approved. These are the same discs that came with your bike when it was brand new. OEM discs are designed to match the exact specifications of your motorcycle, ensuring compatibility and reliable performance.
Pros of OEM Brake Discs:
- Guaranteed Fit and Compatibility: OEM parts are made specifically for your bike model, which means they fit perfectly without modifications.
- Proven Reliability: Since these are the same parts used by the manufacturer, you can expect consistent performance that matches the original setup.
- Warranty Protection: Using OEM parts often maintains your bike’s warranty, which can be voided if you switch to certain aftermarket parts.
Cons of OEM Brake Discs:
- Higher Cost: OEM parts are generally more expensive than their aftermarket counterparts due to branding and manufacturing standards.
- Limited Availability: Depending on your bike model, OEM discs might only be available through dealerships, which can delay repairs if parts are on backorder.
What Are Aftermarket Brake Discs?
Aftermarket brake discs are made by third-party manufacturers and are designed to fit a range of motorcycles, often with enhancements over the stock versions. They can offer better performance, especially for riders looking for specific features like improved heat dissipation or lighter weight.
Pros of Aftermarket Brake Discs:
- Cost-Effective: Typically, aftermarket discs are less expensive than OEM options, making them an attractive choice for budget-conscious riders.
- Variety of Options: You’ll find a wide range of aftermarket discs tailored to different riding styles, such as slotted, drilled, or wave discs for better cooling and reduced weight.
- Performance Upgrades: Many aftermarket discs are designed with enhanced materials or designs to offer superior performance, especially in extreme conditions like racing or heavy touring.
Cons of Aftermarket Brake Discs:
- Potential Compatibility Issues: While many aftermarket discs are designed to fit specific models, slight modifications may be needed for a perfect fit. Always double-check compatibility before buying.
- Inconsistent Quality: The quality of aftermarket discs can vary widely. Some brands offer top-tier performance, while others may compromise on durability. Research is crucial to ensuring you’re getting a reliable product.
- No Warranty Protection: Using aftermarket discs can sometimes void your motorcycle’s warranty, especially if the manufacturer deems them incompatible with the bike’s original setup.
Cost vs. Performance: Which One Offers Better Value?
When choosing between OEM and aftermarket brake discs, consider your priorities. Aftermarket discs are budget-friendly and ideal for daily commuters. OEM discs, on the other hand, ensure a perfect fit and long-term reliability, making them suitable for tourers or riders who prioritize consistency.
For performance seekers, premium aftermarket discs can enhance braking power, cooling, and durability. Just choose reputable brands to avoid safety or longevity issues.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Fit: Verify compatibility to avoid uneven wear or braking inefficiency.
- Purpose: Use OEM for reliability and warranty protection; choose aftermarket for specialized performance needs.
- Warranty: OEM is safer for warranty claims, while aftermarket options may void coverage.
- Durability vs. Cost: Premium aftermarket parts can outperform OEM, but cheaper options might wear faster.
With careful consideration of your budget and riding style, you can choose the option that delivers the best value without compromising safety.
Conclusion
Maintaining your motorcycle’s brake discs is not just about extending their life—it’s about ensuring safety on every ride. From recognizing signs of wear to adopting best practices for upkeep, the steps you take today can save you from costly repairs and dangerous situations in the future.
Prioritize routine inspections, adjust your braking habits, and always invest in quality components suited to your bike and riding style. These small efforts can go a long way in keeping your brake system in top shape and your rides smooth and secure.
We’d love to hear from you! Share your experiences with brake disc maintenance or ask any questions in the comments below. Let’s keep the conversation rolling and help each other stay safe on the road!







