Motorcycle Lost Power While Riding? 8 Causes and Quick Fixes!
Motorcycle Lost Power While Riding? 8 Causes and Quick Fixes!QuoteQ
Motorcycle Lost Power While Riding? 8 Causes and Quick Fixes!QuoteQ
Your motorcycle requires a sufficient and consistent electricity supply to run. Even a single broken wire can cause the whole system to shut down completely. Therefore, if your motorcycle loses all electrical power while riding, components of the electric system are to blame.
In most cases, loose battery terminals, dead batteries, blown fuses, or ignition switch faults cause such power failure. Other possible culprits are broken wires or connectors, rectifier or stator issues, and a bad starter relay. Some potential fixes include replacing the battery, main fuse, ignition switch, or related wires.
Let’s explore the reasons why your motorcycle lost power and how to easily fix it.
Why Does a Motorcycle Lose All Electrical Power While Riding? Fixes and Cost Estimation
As you turn your vehicle, the battery delivers power to the electronics. The wiring harness supplies the generated current to the motorbike parts.
When any components of this system go bad, the vehicle’s power supply is completely cut off. Here are the most common causes behind this power loss:
Loose Battery Terminals or Dead Battery
According to most motorbike owners, the power issue is caused by a dead battery or its terminals. Mechanical impact or corrosion can cause the battery terminals to come loose or disconnect completely. As the circuit is now incomplete, the power supply required to run the vehicle is interrupted.

In case of a dead battery, there is no power at all to start the motorbike. Your battery alternator might be responsible for this. However, a damaged battery cell or expired battery can also be the culprit.
- Diagnosis and Fix
To diagnose loose terminals, locate the motorbike battery from under the seat under the seat or in a compartment on the side. Separate the negative terminal of the battery and make sure it doesn’t touch any metal parts.
- Look for any signs of looseness, corrosion, or damage on the battery terminals and cable clamps. Use a wrench to test the fit. If the terminals are loosened or detached, tighten or replace the metal rings and wires as necessary. Each terminal cost only $3 to $8.
- As for the battery, you can diagnose it with a multimeter. Connect the device and set it to DC voltage mode. Measure the voltage directly at the battery terminals.
- If the reading is significantly lower than 12 volts, it indicates a dead battery. For the replacement, you need a new lithium-ion battery that matches your motorcycle’s specifications. The cost ranges from $75 to $300.
Blown Fuse
Most motorcycles have a 30-amp main fuse and several other fuses for each circuit. Due to electrical surges or overloads, these fuses will blow off to disconnect the power supply.

Your motorcycle will lose power if the blown fuse is protecting a critical circuit like the ignition system or the entire instrument cluster.
- Diagnosis and Fix
A visual inspection is the best way to diagnose blown fuses. Refer to your owner’s manual for the specific location of the fuse box on your motorcycle. It’s usually under the seat, behind a side panel, or near the battery compartment.
When you find any broken or melted filament inside a fuse, use a test light to check for continuity. If the light isn’t lit, pull out the blown fuse with needle-nose pliers. Get a replacement fuse with the same amperage rating, costing $2 to $5 only.
Failed Ignition Switch or Connector
As you turn the ignition key, the ignition switch completes different circuits to provide power to the starter motor, instrument cluster, headlights, etc.

Components of the ignition and the plugged-in electric connectors can corrode or get damaged over time, leading to a complete power loss.
- Diagnosis and Fix
A multimeter will expose the damaged connectors and switch components. Test each part of the ignition switch to check the voltage. Usually low, high, or no voltage at all indicates a failed component.
Remove the fairings, connectors, and switch housing to install a new ignition unit. If necessary, contact an expert mechanic. Overall, you need to pay $7 to $25 for an ignition switch and about $100 for labor.
Broken Wires or Connectors
Your motorcycle relies on a network of wires and connectors to transmit electrical current from the battery to power various components.

A broken or frayed wire or connector in the system disrupts electricity flow. It can cause the whole system to shut off while driving.
- Diagnosis and Fix
First, perform a visual inspection to locate any exposed wires, signs of chafing or fraying on the wire insulation, or burnt or melted wires and connectors. Pay special attention to all the ground wires.
- You can use a multimeter for voltage checks at different points in the circuit to pinpoint the break or faulty connection.
- To fix the problem, tighten any loose connectors and replace the fully damaged ones. For broken wires, try soldering or crimping the wires back together using a heat shrink sleeve for insulation. It will only cost you around $10.
Bad Starter Relay/Solenoid
When you press the ignition button, the starter relay or solenoid acts like a switch that controls the flow of high current from the battery to the starter motor.
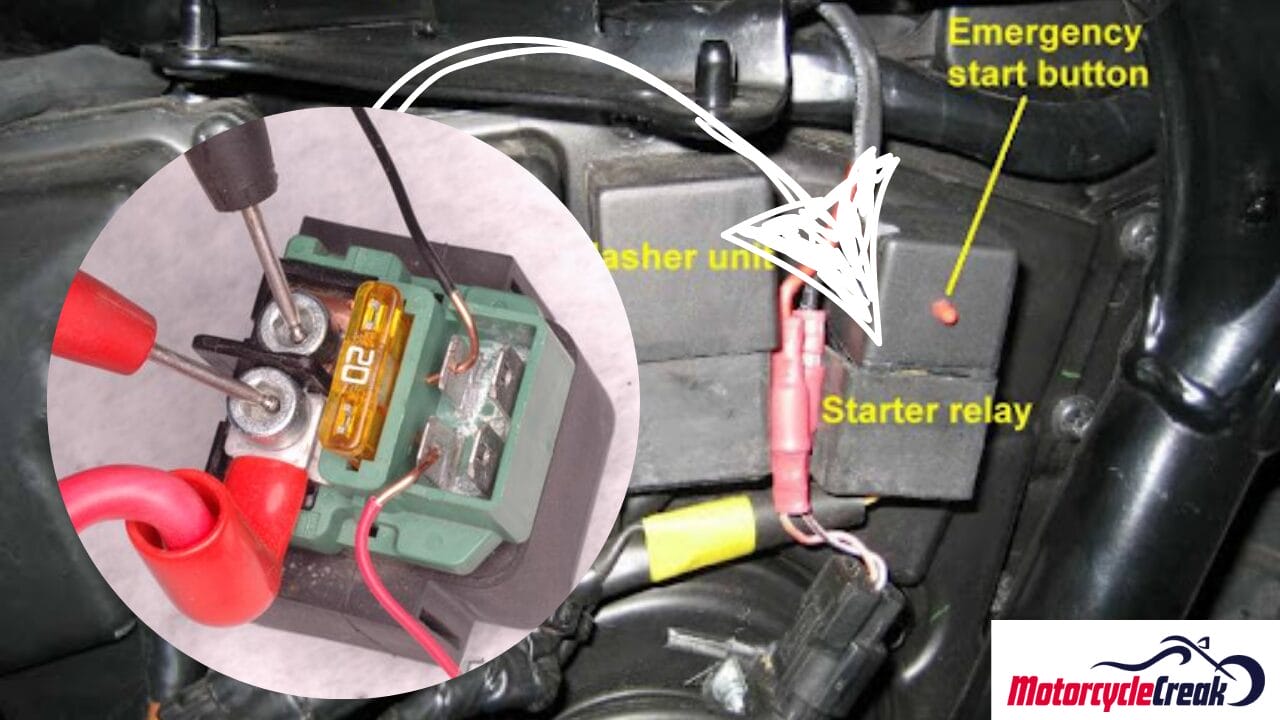
The internal components of the relay, such as the coil or contacts, can wear out, corrode, or malfunction. It prevents the starter motor from getting sufficient power, causing the engine to turn off eventually.
- Diagnosis and Fix
Perform a solenoid click test to diagnose the faulty part. If you hear a clicking sound upon starting the vehicle but the engine doesn’t crank, it’s a sign of a failing relay. However, a clicking sound can also indicate other issues like a dead battery or starter motor problems.
- To be sure, find the starter relay located below the seat and test it for continuity with a multimeter. If it has no voltage, consider getting a replacement costing $5 to $40.
- First, disconnect all the wires and connectors from the relay. Use a wrench to take off the mounting bolts connecting the relay to the frame. Pull the old starter out and fit the new one in its housing.
Rectifier or Stator Issues
To keep your motorcycle running, you must have a functioning charging system. A stator and rectifier regulator are the two main parts of this system that generate AC electricity and convert it to DC.

Any malfunction of the two parts leads to undercharging or overcharging of the battery. As a result, the battery cells can get damaged and cause a complete loss of electric power.
- Diagnosis and Fix
For initial diagnosis, check if your battery voltage is unusually higher or lower than 12 volts. However, diagnosing and fixing the charging system components is a complex and lengthy process.
Hence, it’s best to leave it to the professionals. For each part, you need to pay $150 to $350, whereas the labor cost starts from $100.
Wrapping Up!
Failure to generate or deliver electricity to the motor parts is the reason why your motorcycle loses all electrical power while riding. Thankfully, it’s not an expensive repair and anyone with previous experience of troubleshooting a motorcycle can fix it at home.
If you’re lucky, replacing the battery, fuse, or damaged wires will get your motorbike power back. However, for more complicated parts like the stator or rectifier, make sure to take your vehicle to an expert mechanic to fix the issue without damaging any sensitive parts.







